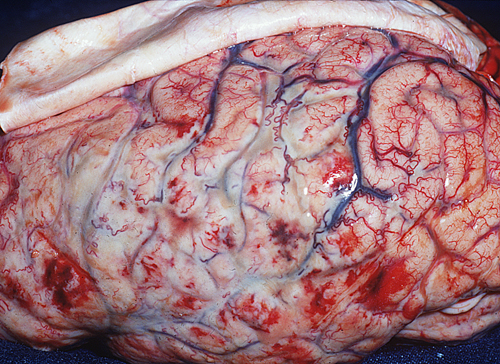
A craniotomy is a surgery in which part of the skull bone is removed in order to expose the brain and the structures of the central nervous system, the bone flap is temporarily removed and the end of the surgery is repositioned to give new protection the brain and its structures.
It is important to differentiate it from the craniectomy, which is a similar procedure that involves the permanent removal of the skull, in order to make room for the brain when there is significant inflammation.
A craniotomy may be performed for different reasons, such as to treat the following diseases:
Resection of brain tumors
Repair of brain aneurysms
Removing both subdural, epidural or intracerebral hematomas.
Treatment of congenital arteriovenous malformations
Brain abscess drainage
Repair skull fractures secondary to trauma
Repair of the membranes covering the brain (dura) when there
Cerebrospinal fluid leak.
A craniotomy may be performed in any of the skull and is named according to the part of the bone is resected, so craniotomy may involve one, two or even three combination skull bones and calling for example, frontal craniotomy if is only the frontal bone, frontotemporal craniotomy if the front part of the temporal bone and which is resected or excised if frontoparietotemporal craniotomy of the frontal, parietal and temporal bone.
The procedure is performed with the patient completely asleep with general anesthesia. The position depends on the site where it will perform a craniotomy, can be placed face up, face down, sideways, his head turned to one side or another etc. in any case, the fixation of the head is necessary to prevent movement during surgery.
Decontamination of the surgical site with bactericidal substances is performed and proceeds with aseptic technique to incision of the scalp and may be linear, curved or horseshoe provided in area where hair grows, for cosmetic issues
Craniotome a hole using a bone from which extends a wide enough window of bone (craniotomy) to adequately treat any injury is done. Immediately below are bone coverage of the brain called the meninges, the outermost of which the dura and the rest must be opened to perform the required treatment for each patient
As with any surgical procedure, complications may arise, among which include, but are not limited to:
• nervous system infection or wound
• hemorrhage (bleeding)
• thrombi (blood clots)
• CSF leak
• damage to blood vessels that may condition infarcts
• slurred speech, strength, mobility and coordination of the limbs.
• Alterations to walk
• death
In my personal opinion, I can say that this surgery is one of the most interesting in the field of neurology as it involves many immersed procedures into one, for me is the most beautiful because it takes many hours of surgery and requires a lot accuracy to conclude successfully
Recovered of http://www.cirugia-neurologica.org/cirugia-cerebral.ws on 30th October,2015 at 15:00
Rebeca L. Guzmán L.